September 24 is the 267th day of the year (268th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 98 days remaining until the end of the year
Holidays
- Armed Forces Day (Peru)
- Christian feast day:
- Constitution Day (Cambodia)
- Heritage Day (South Africa).
- Independence Day (Guinea-Bissau), celebrates the independence of Guinea-Bissau from Portugal in 1973.
- Mahidol Day (Thailand)
- New Caledonia Day (New Caledonia)
- Republic Day (Trinidad and Tobago)
- Start of the indiction year (Late Roman Empire; at least since the time of Bede)
- National Punctuation Day (United States)
History
In 768, Charlemagne is crowned the first King of the Franks.

In 768, In order for Charlemagne to become king, Pepin the Short, Frankish king (b. 714) had to die. He was the King of the Franks from 751 until his death. He was the first of the Carolingians to become king. The younger son of the Frankish prince Charles Martel and his wife Rotrude, Pepin’s upbringing was distinguished by the ecclesiastical education he had received from the monks of St. Denis. Succeeding his father as the Mayor of the Palace in 741, Pepin reigned over Francia jointly with his elder brother Carloman. Pepin ruled in Neustria, Burgundy, and Provence, while his brother Carloman established himself in Austrasia, Alemannia and Thuringia. The brothers were active in suppressing revolts led by the Bavarians, Aquitanians, Saxons, and the Alemanni in the early years of their reign. In 743, they ended the Frankish interregnum by choosing Childeric III, who was to be the last Merovingian monarch, as figurehead king of the Franks.
Being well disposed towards the church and Papacy on account of their ecclesiastical upbringing, Pepin and Carloman continued their father’s work in supporting Saint Boniface in reforming the Frankish church, and evangelising the Saxons. After Carloman, who was an intensely pious man, retired to religious life in 747, Pepin became the sole ruler of the Franks. He suppressed a revolt led by his half-brother Grifo, and succeeded in becoming the undisputed master of all Francia. Giving up pretense, Pepin then forced Childeric into a monastery and had himself proclaimed king of the Franks with support of Pope Zachary in 751. The decision was not supported by all members of the Carolingian family and Pepin had to put down a revolt led by Carloman’s son, Drogo, and again by Grifo.
As King, Pepin embarked on an ambitious program to expand his power. He reformed the legislation of the Franks and continued the ecclesiastical reforms of Boniface. Pepin also intervened in favour of the Papacy of Stephen II against the Lombards in Italy. He was able to secure several cities, which he then gave to the Pope as part of the Donation of Pepin. This formed the legal basis for the Papal States in the Middle Ages. The Byzantines, keen to make good relations with the growing power of the Frankish empire, gave Pepin the title of Patricius. In wars of expansion, Pepin conquered Septimania from the Islamic Umayyads, and subjugated the southern realms by repeatedly defeating Waifer of Aquitaine and his Basque troops, after which the Basque and Aquitanian lords saw no option but to pledge loyalty to the Franks. Pepin was, however, troubled by the relentless revolts of the Saxons and the Bavarians. He campaigned tirelessly in Germany, but the final subjugation of these tribes was left to his successors.
Pepin died in 768 and was succeeded by his sons Charlemagne and Carloman. Although unquestionably one of the most powerful and successful rulers of his time, Pepin’s reign is largely overshadowed by that of his more famous son.
In 787, Second Council of Nicaea: The council assembles at the church of Hagia Sophia.
In 1180, Manuel I Komnenos, last Emperor of the Komnenian restoration dies. The Byzantine Empire slips into terminal decline.
In 1645, Battle of Rowton Heath, Parliamentarian victory over a Royalist army commanded in person by King Charles
In 1664, The Dutch Republic surrenders New Amsterdam to England.
In 1674, Second Tantrik Coronation of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.

In 1780, Benedict Arnold flees to British Army lines when the arrest of British Major John André exposes Arnold’s plot to surrender West Point.
In 1789, The United States Congress passes the Judiciary Act which creates the office of the United States Attorney General and the federal judiciary system, and orders the composition of the Supreme Court of the United States.
In 1830, Belgian Revolution: A revolutionary committee of notables forms the Provisional Government of Belgium.
In 1852, The first airship powered by (a steam) engine, created by Henri Giffard, travels 17 miles (27 km) from Paris to Trappes.
In 1853, Admiral Despointes formally takes possession of New Caledonia in the name of France.
In 1841, The Sultan of Brunei cedes Sarawak to the United Kingdom.
In 1869, “Black Friday“: Gold prices plummet after Ulysses S. Grant orders the Treasury to sell large quantities of gold after Jay Gould and James Fisk plot to control the market.

In 1889, D. H. Hill, American general and academic (b. 1821) dies at Charlotte, N. C. and was buried in Davidson College Cemetery. He was a Confederate general during the American Civil War and a Southern scholar. He is usually referred to as D.H. Hill, in part to distinguish him from unrelated Confederate general A.P. Hill, who served with him in the Army of Northern Virginia.
He was known as an aggressive leader, and as an austere, deeply religious man, with a dry, sarcastic humor. He was brother-in-law to Stonewall Jackson, a close friend to both James Longstreet and Joseph E. Johnston, but disagreements with both Robert E. Lee and Braxton Bragg cost him favor with Confederate President Jefferson Davis. Although his military ability was well respected, he was underutilized by the end of the Civil War on account of these political feuds.
From 1866 to 1869, Hill edited a magazine, The Land We Love, at Charlotte, North Carolina, which dealt with social and historical subjects, and had a great influence in the South. In 1877, he became one of the first presidents of the University of Arkansas, a post that he held until 1884, and, in 1885, president of the Military and Agricultural College of Milledgeville, Georgia until August 1889, when he resigned due to failing health.
In 1890, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints officially renounces polygamy.
In 1877, Battle of Shiroyama, decisive victory of the Imperial Japanese Army over the Satsuma Rebellion
In 1906, U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt proclaims Devils Tower in Wyoming as the nation’s first National Monument.
In 1914, World War I: The Siege of Przemyśl (present-day Poland) begins.
In 1932, Gandhi and Dr. B. R. Ambedkar agree to the Poona Pact, which reserved seats in the Indian provincial legislatures for the “Depressed Classes” (Untouchables).

In 1935, Earl Bascom and Weldon Bascom produce the first rodeo ever held outdoors under electric lights at Columbia, Mississippi
In 1946, Cathay Pacific Airways is founded in Hong Kong.
In 1946, Clark Clifford and George Elsey, military advisers to U.S. President Harry S. Truman, present him with a top-secret report on the Soviet Union that first recommends the containment policy.
In 1948, The Honda Motor Company is founded.
In 1950, Forest fires black out the sun over portions of Canada and New England. A blue moon is seen as far away as Europe.
In 1957, Camp Nou, the largest stadium in Europe, is opened in Barcelona.
In 1957, President Dwight D. Eisenhower sends 101st Airborne Division troops to Little Rock, Arkansas, to enforce desegregation.

In 1960, USS Enterprise (CVN-65), the world’s first nuclear-powered aircraft carrier, is launched.
In 1962, United States court of appeals orders the University of Mississippi to admit James Meredith.
In 1968, Swaziland joins the United Nations.
In 1968, 60 Minutes debuts on CBS.
In 1973, Guinea-Bissau declares its independence from Portugal.
In 1979, CompuServe launches the first consumer internet service, which features the first public electronic mail service.
In 1990, Periodic Great White Spot is observed on Saturn.
In 1996, Representatives of 71 nations sign the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty at the United Nations.
In 2005, Hurricane Rita makes landfall in the United States, devastating Beaumont, Texas and portions of southwestern Louisiana.
In 2007, Between 30,000 and 100,000 people take part in anti-government protests in Yangon, Burma, the largest in 20 years.
In 2009, The G20 summit begins in Pittsburgh with 30 global leaders in attendance. It marks the first use of LRAD in U.S. history.
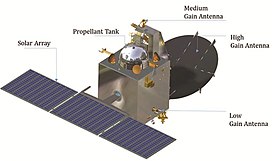
In 2014, The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), a Mars orbiter launched into Earth orbit by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), successfully inserted into orbit of Mars.
In 2015, At least 1,100 people are killed and another 934 wounded after a stampede during the Hajj in Saudi Arabia.

